1. What is 5G?
Mobile network operators (MNOs) have two main options to choose from when deploying 5G: non-standalone (NSA) and standalone (SA).
NSA dominated as the top choice for initial 5G deployments among MNOs, thanks to existing cellular infrastructure. But, as SA 5G deployments take off, it's important to understand the distinctions between the two.
Both NSA and SA use the 5G New Radio (5G NR) interface, enabling them to deliver features and capabilities based on the standards defined by the 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP). 5G NR offers myriad use cases, but one of its most essential features is it provides a path from 4G LTE to 5G.
2. What is Non-standalone 5G (NSA)
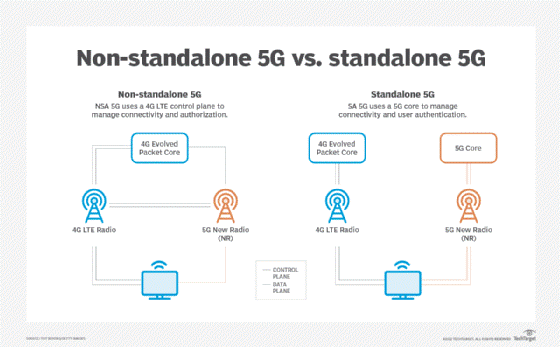
5G non-standalone (NSA) is the first version of 5G network architecture, considered to be a “steppingstone” to the “true” 5G network that is 5G standalone (SA). As the name suggests, 5G NSA is not “standalone”, meaning it is designed to be deployed on top of existing 4G LTE network infrastructure.
Globally, 5G NSA has been primarily used by wireless carriers to quickly and easily deliver 5G services to end users.
3. What is 5G Standalone (SA)
5G standalone (SA) is a completely new mobile network architecture. It enables all of the capabilities of 5G, given that it is not dependent on any existing 4G LTE infrastructure.
5G SA involves a new 5G packet core architecture, which means that 5G services can be deployed without pre-existing 4G LTE equipment in the network.
4. Differences between NSA and SA
The main difference of NSA (Non-Standalone Architecture) and SA (Standalone Architecture) is that NSA anchors the control signaling of 5G Radio Networks to the 4G Core, while the SA scheme connects the 5G Radio directly to the 5G core network, and the control signaling does not depend on the 4G network at all. NSA, as the name suggests, is a 5G service that does not ‘stand alone’ but is built over an existing 4G network. SA, on the other hand, allows completely independent operation of a 5G service without any interaction with an existing 4G core.
5. 5G testing in Vietnam
Vietnam's Ministry of Information and Communications (MIC) issued three technical regulations related to 5G technology for mobile devices: QCVN 127:2021/BTTTT; QCVN 127:2021/BTTTT and QCVN 18:2022/BTTTT.
- QCVN 127:2021/BTTTT: National technical regulation on Standalone 5G user equipment- Radio access.
- QCVN 129:2021/BTTTT: National technical regulation on Non- Standalone 5G user equipment- Radio access.
- QCVN 18:2022/BTTTT: National technical regulation on Electromagnetic Compatibility for Radio equipment.
On May 31, 2023, MIC issued Circular 04/2023/TT-BTTTT providing list of products and goods that have the possibility to cause safety under the management responsibility of the MIC.
On Sep 05, 2023, MIC issued Circular 10/2023/TT-BTTTT, pending of application of regulations on partial/full implementation of some technical regulations in Circular 04/2023/TT-BTTTT. That mean from Jan 01, 2024, mobile devices using 5G technology have to get TAC.
Dt&C Vina .,JSC was assigned for 5G testing by MIC according to Decision no. 2024/QĐ-BTTTT, Dt&C Vina is the first and only laboratory in Vietnam who can conduct 5G testing for mobile devices.
For more detail, please contact Dt&C Vina via email: info@dtnc.vn or hotline: 0862.619.168








![[MIC] Officially issued QCVN 134:2024/BTTTT - National technical regulation on specific absorption levels for handheld and body-worn radio devices according to Circular 19/2024/TT-BTTTT of Ministry of Information and Communications](https://cdn0577.cdn4s.com/thumbs/qcvn-134_thumb_150.jpg)



![[Latest] Circular 02/2024/TT-BTTTT regulating the List of potentially unsafe products and goods under the management responsibility of the Ministry of Information and Communications](https://cdn0577.cdn4s.com/thumbs/trang-huy-hieu-the-loai-logo-2_thumb_150.jpg)