1. What is Safety?
The increase of the electrical equipment in homes, offices, hospitals and industrial areas makes it so important to protect human life and property from fire, electric shock, injury and hazardous radiation energy. Consequently, manufacturers of many industries including information and communication equipment, medical equipment, home appliances and industrial machinery, etc. are able to enter the market only if they meet safety standards and regulations in each country.
Fire hazards, electrical shock, injury, energy, radiation and mechanical/chemical risk caused by overheating, electrical leakage current, insulation aging, radiation, UV radiation, and mechanical risk from electronic products threatens human life and property. As a result, countries around the world makes it mandatory to conduct safety tests and all appliances on the market have to demonstrate safety through testing in accordance with the safety standards of your country.
The compliance of safety standards is mandatory in major worldwide markets. Safety test is an essential process to meet the legal requirements and reduce the risk from the product.
2. Main Test items in Safety
| No. | Name of test items | Summary of test |
| 1 | Input test | During normal operation, it is to test/evaluate whether the rated current or rated power indicated on the label is within the appropriate range specified in the standard. |
| 2 | Heating test | In normal operation, it is to test/evaluate whether the temperature measured on the exterior and internal components of the product meets the limit values specified in the standard. |
| 3 | Withstanding voltage test | It is to test/evaluate the insulation performance of the insulation materials used inside/outside the product. |
| 4 | Leakage current test (or touch current test) | It is to test/evaluate whether the current leaking from the product is safe from the risk of electric shock. |
| 5 | Abnormal operation test | After reviewing the possibility of abnormal operation of the product, it is to test/evaluate whether the product is safe in the abnormal operation condition by making an artificial defect state. |
| 6 | Fault condition test | After reviewing the possibility of fault, it is to test/evaluate whether the product is safe from the risks of electric shock and fire by electrically shorting or opening the electrical component or protection device in the circuit of the product. |
| 7 | Ball pressure test | It is to test/evaluate the softening temperature and accelerated material flow under loading of polymeric materials and parts of end product in their ability to resist abnormal heat. |
| 8 | Flammability test | This is to test/evaluation the flame retardancy of plastic materials that are vulnerable to fire, and the flammability class is graded according to its own extinguishing time. |
| 9 | Glow wire test | This is a test to evaluate the flame retardancy of plastic enclosures of end product and plastic materials supporting current-carrying conductors, which are susceptible to fire. When the glow wire according to the temperature specified in the standard is applied to the specimen, the suitability is evaluated by the height of the generated flame and the self-extinguishing time. |
| 10 | Needle flame test | It is to simulate the effect of a small flame which may result from fault conditions, in order to assess by a simulation technique the fire hazard, and this test is applied to electrotechnical equipment, its sub-assemblies and components and to solid electrical insulating materials or other combustible materials. |
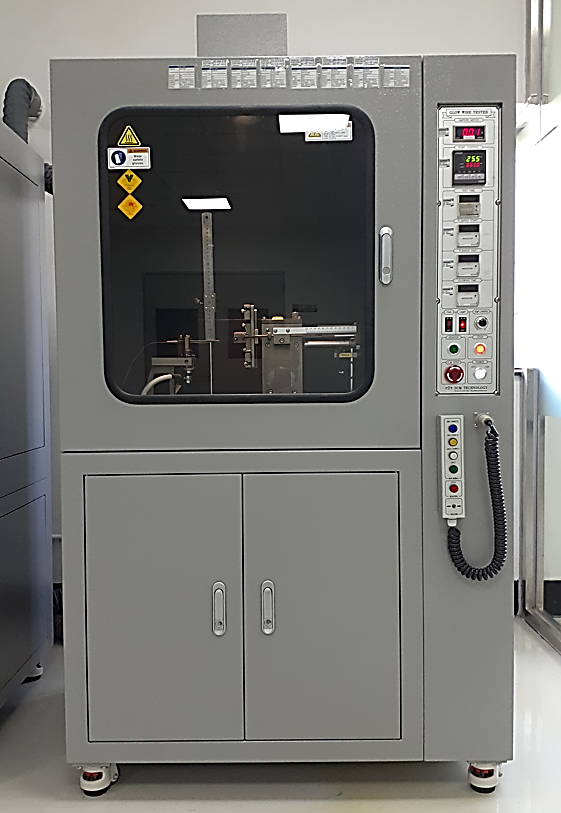
| 11 | Tracking resistance test | It is to test for the determination of the proof and comparative tracking indices of plastic insulating materials on pieces taken from parts of product and on the prescribed specimens using AC voltages. In addition, this test is a test to find out the voltage generated by tracking when 50 drops of the test solution is dropped on the specimen, and this result is used as a factor in determining the creepage distance. |
3. Major test equipment
 |  | 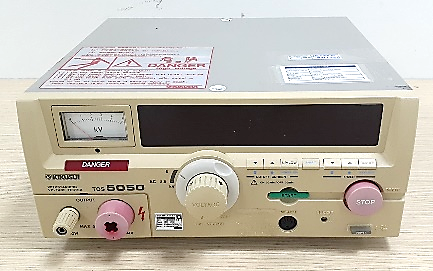 |
| (Power Meter) | (Earth continuity tester) | (Withstanding voltage tester) |
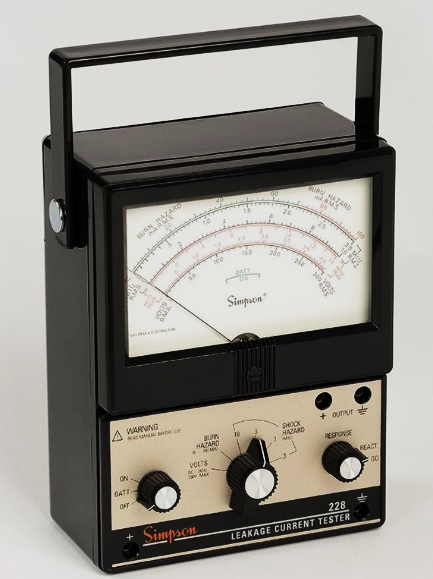 |  | 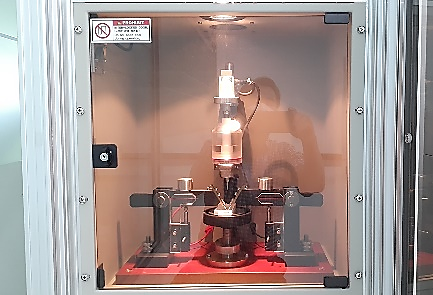  |
| (Leakage current tester) | (Environmental chamber) | (Tracking tester) |
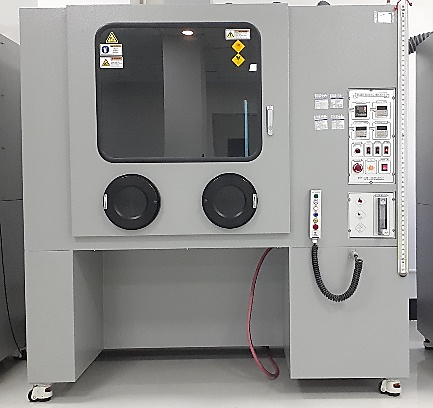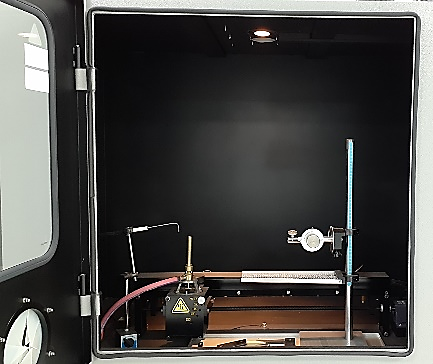  |   | 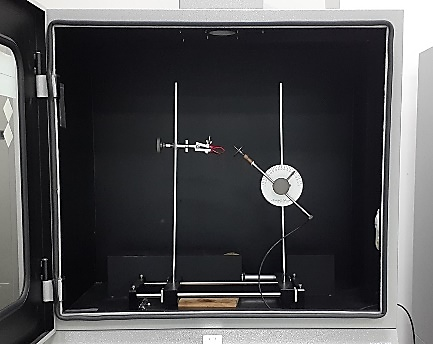  |
| (Flammability tester) | (Glow wire tester) | (Needle flame tester) |
 |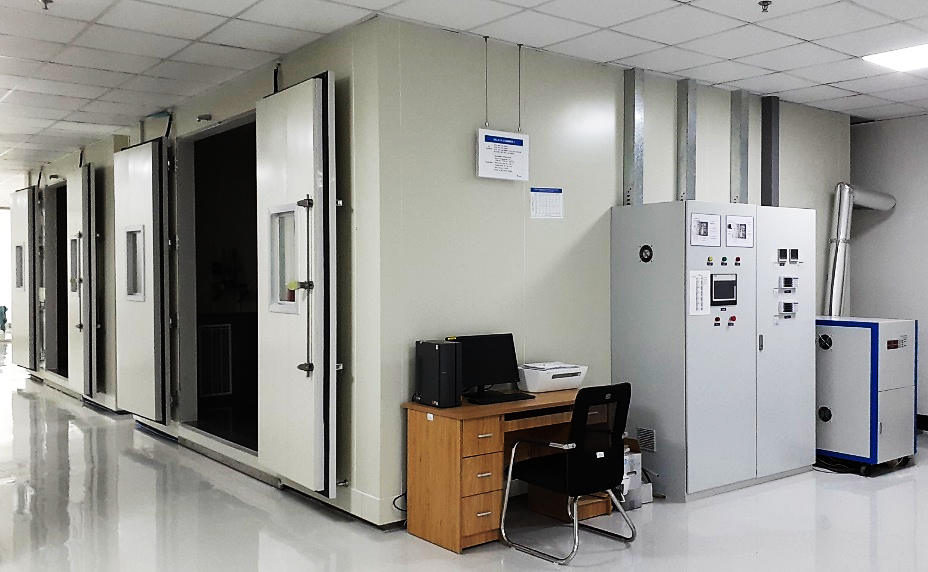  | |
| (Power source, 80 kVA) | (Walk-in chamber) | |
4. Certification Schemes
| Certification Schemes | Process / Contents | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
(Vietnam / CR certification) | (1) Scopes 1) QCVN 4: Household appliances 2) QCVN 19: LED luminaires (2) The period of validity of certification 1) Method 1: 3 years 2) Method 5: 3 years (maintaining certification through F/U inspection) 3) Method 7: Valid for the batch only. (3) Certification methods
| ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
(Korea / KC Certification) | (1) Safety certification program 1) The manufacturer or importer of a product that is subject to the requirement of safety certification must receive the safety certification as per the Decree by the Ministry of Trade, Industry, and Energy. This program also requires that the factory must be inspected in order to ensure that the product's quality can be maintained, as well as the inspection of the products themselves for their compliance with safety criteria so that the safety of the product in question can be verified before it is shipped. 2) Regular inspections (2) Safety confirmation reporting program (3) Supplier Qualification Confirmation Report
(The process of supplier conformance confirmation) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
(China / CCC certification) | (1) Introduction CCC is a compulsory certification scheme, including product inspection, which has been conducted since 2001 to protect consumers in China. If any product produced in China or exported to China is subject to compulsory certification, it must be certified safe and quality in accordance with IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission) and Chinese national standards. (2) Product scope
(3) Certification process Application to the certification body ⇨ Document review ⇨ Type test ⇨ Factory audit ⇨ Comprehensive evaluation of the certification body ⇨ Issuance of certificates and certification marks ⇨ Post-Inspection and Management | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
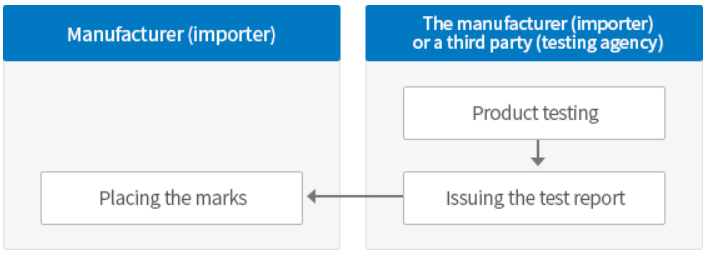
(Europe / CE marking) | (1) Introduction CE stands for “Conformité Européenne”, which in practice means that it “conforms to European directives”. CE marking of a product means that it complies with the legal requirements placed on the product within the EEA and therefore can be sold there. The manufacturer or their authorized representative gives the product its CE marking and is liable for ensuring that the product complies with the requirements of the directives. (2) EU Directives For electrical and electronic products the below 10 directives are the most commonly used: ▪ Low Voltage Directive (LVD) 2014/35/EU ▪ EMC Directive 2014/30/EU ▪ Radio Equipment Directive (RED) 2014/53/EU ▪ Restriction of the use of certain hazardous substances (RoHS), Directive 2011/65/EU ▪ Energy related Products Directive (ErP) 2009/125/EC ▪ Maritime Equipment Directive (MED) 2014/90/EU ▪ Equipment and protective systems intended for use in potentially explosive atmospheres (ATEX) 2014/34/EU ▪ Medical Device Regulation (MDR) 2017/745/EU ▪ Construction Products Regulation 305/2011/EU (CPR) ▪ Machinery Directive (MD) 2006/42/EC (3) DoC and CoC for CE marking 1) DoC: It means a declaration of conformity, which is usually submitted in a form made by the manufacturer itself. Product testing can be carried out by the manufacturer itself or by using a testing laboratory to test according to the specified specifications. (However, in general, the manufacturer does not have the facilities and manpower that can test according to the standard, so a test laboratory is used.) 2) CoC: It means a certificate of conformity, and is usually issued by testing a product based on the test standards prescribed by a testing laboratory designated by the competent authority (ex: Notified Body). | ||||||||||||||||||||||
5. Certification Marks Supportable
| Regional | Country / Certification name | |||
| Asia/Oceania |  |  |  | |
| Vietnam / CR | Korea / KC | China / CCC | Japan / PSE | |
 |  |  |   | |
| Indonesia / SNI | Malaysia / SIRIM | Singapore / CPS | Thailand / TISI | |
 | -- | -- | -- | |
| Australia / RCM | -- | -- | -- | |
| America |  |  |  |  |
| USA / UL | USA / TUV | USA / ETL | USA / MET | |
 |  |  |  | |
| Canada / CSA | Argentina / IRAM | Mexico / NOM | Chile / SEC | |
| Europe |  |  |  |  |
| EU / CE | UK / UKCA | Germany / GS | Germany / VDE | |
 |  |     |  | |
| EU / ENEC | Germany / TUV bauart | Nordic countries / FIMKO, DEMKO, NEMKO, SEMKO | France / OVE | |
| Middle East |  | |||
| Gulf countries (Saudi Arabia, Kuwait, UAE, Quatar, Bahrain, Orman) / GCC | ||||
| Africa | No certification mark | No certification mark | No certification mark | -- |
| South Africa / LOA | Ethiopia / CoC | Egypt / CoC | -- | |










![[MIC] Officially issued QCVN 134:2024/BTTTT - National technical regulation on specific absorption levels for handheld and body-worn radio devices according to Circular 19/2024/TT-BTTTT of Ministry of Information and Communications](https://cdn0577.cdn4s.com/thumbs/qcvn-134_thumb_150.jpg)



![[Latest] Circular 02/2024/TT-BTTTT regulating the List of potentially unsafe products and goods under the management responsibility of the Ministry of Information and Communications](https://cdn0577.cdn4s.com/thumbs/trang-huy-hieu-the-loai-logo-2_thumb_150.jpg)