The ECE R10 is an international regulation regarding electromagnetic compatibility of vehicles of the following categories:
-
L: Motor vehicles with less than four wheels
-
M: Power-driven vehicles having at least four wheels and used for the carriage of passengers
-
N: Power-driven vehicles having at least four wheels and used for the carriage of goods
-
O: Trailers (including semi–trailers)
-
T, R, S: Agricultural vehicles
What is the UNECE R10?
The UNECE Regulation No. 10 is about electromagnetic compatibility for the automotive industry. It states that every vehicle and every electronic sub-assembly (ESA) that is sold in any of the UNECE member countries should be compliant with the UNECE R10 requirements.
The most recent and updated the version of Regulation 10 is revision 6 from 2019 (ECE/TRANS/WP.29/2019/20).
The UNECE R10 concerns the adoption of harmonized technical United Nations Regulations for wheeled vehicles, equipment and parts which can be fitted and/or be used on wheeled vehicles and the conditions for reciprocal recognition of approvals granted based on these United Nations Regulations. More specifically, this UNECE R10 applies to the following elements:
-
Vehicles of categories L, M, N O, T, R and S with regard to electromagnetic compatibility. This includes two- and three-wheeled motorcycles, mopeds, electric bicycles, four-wheeled (or more) vehicles for carrying passengers or cargo, and trailers (including semitrailers).
-
Components and separate technical units intended to be fitted in these vehicles with regard to electromagnetic compatibility.
The UNECE Regulation No. 10 is applied by the following countries: Germany, France, Italy, Netherlands, Sweden, Belgium, Hungary, Czech Republic, Spain, Serbia, United Kingdom, Austria, Luxembourg, Switzerland, Norway, Finland, Denmark, Romania, Poland, Portugal, Russian Federation, Greece, Ireland, Croatia, Slovenia, Slovakia, Belarus, Republic of Mo.dova, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Latvia, Bulgaria, Kazakhstan, Lithuania, Turkey, Azerbaijan, Nortz Macedonia, European Union, Japan, Australia, Ukraine, South Africa, New Zealand, Cyprus, Malta, Republic of Korea, Malaysia, Thailand, Albania, Armenia, Montenegro, San Marino, Tunisia, Georgia, Egypt, Nigeria, Pakistan.
Automotive EMC standards
The UNECE R10 refers to many EMC standards to define the limits and the test set-ups:
-
CISPR 12 "Vehicles', motorboats' and spark-ignited engine-driven devices' radio disturbance characteristics - Limits and methods of measurement", fifth edition 2001 and Amd1: 2005.
-
CISPR 16-1-4 "Specifications for radio disturbance and immunity measuring apparatus and methods - Part 1: Radio disturbance and immunity measuring apparatus apparatus - Antennas and test sites for radiated disturbances measurements", third edition 2010.
-
CISPR 25 "Limits and methods of measurement of radio disturbance characteristics for the protection of receivers used on board vehicles", second edition 2002 and corrigendum 2004.
-
ISO 7637-2 "Road vehicles - Electrical disturbance from conduction and coupling - Part 2: Electrical transient conduction along supply lines only on vehicles with nominal 12 V or 24 V supply voltage", second edition 2004.
-
ISO-EN 17025 "General requirements for the competence of testing and calibration laboratories", second edition 2005 and Corrigendum: 2006.
-
ISO 11451 "Road vehicles - Electrical disturbances by narrowband radiated electromagnetic energy - Vehicle test methods": Part 1: General and definitions (ISO 11451-1, third edition 2005 and Amd1: 2008); Part 2: Off-vehicle radiation source (ISO 11451-2, fourth edition 2015); Part 4: Bulk current injection (BCI) (ISO 11451-4, third edition 2013).
-
ISO 11452 "Road vehicles - Electrical disturbances by narrowband radiated electromagnetic energy - Component test methods": Part 1: General and definitions (ISO 11452-1, third edition 2005 and Amd1: 2008); Part 2: Absorber-lined chamber (ISO 11452-2, second edition 2004); Part 3: Transverse electromagnetic mode (TEM) cell (ISO 11452-3, third edition 2016); Part 4: Bulk current injection (BCI) (ISO 11452-4, fourth edition 2011); Part 5: Stripline (ISO 11452-5, second edition 2002).
-
ITU Radio Regulations, edition 2008.
-
IEC 61000-3-2 "Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) - Part 3-2 - Limits for harmonic current emissions (equipment input current ≤ 16 A per phase)", edition 3.2 - 2005 + A1: 2008 + A2: 2009.
-
IEC 61000-3-3 "Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) - Part 3-3 - Limits - Limitation of voltage changes, voltage fluctuations and flicker in public low-voltage systems for equipment with rated current ≤ 16 A per phase and not subjected to conditional connection", edition 2.0 - 2008.
-
IEC 61000-3-11 "Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) - Part 3-11 - Limits - Limitation of voltage changes, voltage fluctuations and flicker in public low-voltage systems - Equipment with rated current ≤ 75 A per phase and subjected to conditional connection", edition 1.0 - 2000.
-
IEC 61000-3-12 "Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) - Part 3-12 - Limits for harmonic current emissions produced by equipment connected to public low-voltage systems with input current > 16 A and ≤ 75 A per phase", edition 1.0 - 2004.
-
IEC 61000-4-4 "Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) - Part 4-4 - Testing and measurement techniques - Electrical fast transients/burst immunity test", edition 2.0 - 2004.
-
IEC 61000-4-5 "Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) - Part 4-5 - Testing and measurement techniques - Surge immunity test", edition 2.0 - 2005.
-
IEC 61000-6-3 "Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) - Part 6-3 - Generic standards Emission standard for residential, commercial and light-industrial environments", edition 2.0 - 2006.
-
CISPR 16–2–1 "Specification for radio disturbances and immunity measuring apparatus and methods - Part 2-1 - Methods of measurement of disturbances and immunity - Conducted disturbances measurement", edition 2.0 - 2008.
-
CISPR 22 "Information Technology Equipment - Radio disturbances characteristics - Limits and methods of measurement", edition 6.0 - 2008.
-
CISPR 16-1-2 "Specification for radio disturbance and immunity measuring apparatus and methods - Part 1-2: Radio disturbance and immunity measuring apparatus - Ancillary equipment - Conducted disturbances", edition 2 2014.
-
IEC 61851-1 "Electric vehicle conductive charging system – Part 1: General requirements ", edition 3.0 - 2017
-
CISPR 32 "Electromagnetic compatibility of multimedia equipment – Emission requirements”, edition 2.0 – 2015.
Application for approval
1. Vehicle type approval
- It must be submitted by the vehicle manufacturer.
- The manufacturer must provide a schedule describing all relevant vehicle electrical/electronic systems or ESAs, body styles, variations in body material, general wiring arrangements, engine variations, left-hand/right-hand drive versions and wheelbase versions. Relevant vehicle electrical/electronic systems or ESAs are those which may emit significant broadband or narrowband radiation and/or those which are involved in immunity related functions of the vehicle and those which provide coupling systems for charging the REESS.
- A vehicle, which has to be representative of the type approved, shall be selected from the submitted schedule by mutual agreement between the manufacturer and the Type Approval Authority.
- One or more vehicles might be selected if it is considered that different electrical/electronic systems are included which are likely to have a significant effect on the vehicle’s EMC compared with the fist representative vehicle.
- For vehicles of categories L6, L7, M, N, O, T, R and S, the vehicle manufacturer shall provide a statement of frequency bands, power levels, antenna positions and installation provisions for the installation of radio frequency transmitters (RF-transmitters), even if the vehicle is not equipped with an RF transmitter at time of type approval. This should cover all mobile radio services normally used in vehicles. This information shall be made publicly available following the type approval.
- Vehicle manufacturers shall provide evidence that vehicle performance is not adversely affected by such transmitter installations.
2. ESA type approval
Manufacturers must check the applicability of the UNECE R10 regulation to an ESA following the next flowchart:
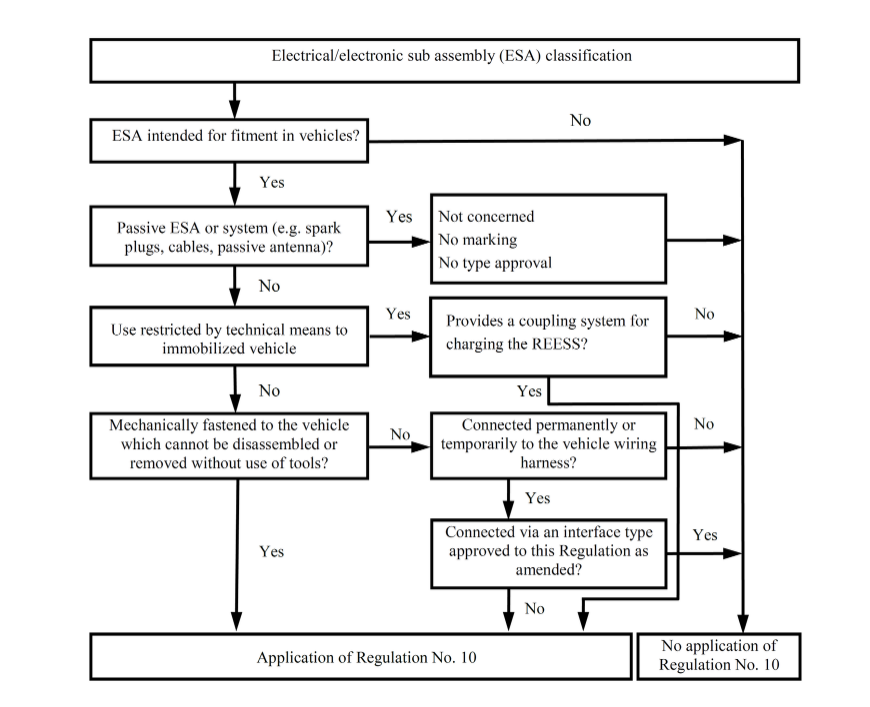
-
The application for approval of a type of ESA shall be submitted by the vehicle manufacturer or by the manufacturer of the ESA
-
The manufacturer may supplement the application with a report on tests which have been carried out. Any such data provided may be used by the Type Approval Authority for the purpose of drawing up the communication form for type approval.
Source: academyofemc.com







![[MIC] Officially issued QCVN 134:2024/BTTTT - National technical regulation on specific absorption levels for handheld and body-worn radio devices according to Circular 19/2024/TT-BTTTT of Ministry of Information and Communications](https://cdn0577.cdn4s.com/thumbs/qcvn-134_thumb_150.jpg)



![[Latest] Circular 02/2024/TT-BTTTT regulating the List of potentially unsafe products and goods under the management responsibility of the Ministry of Information and Communications](https://cdn0577.cdn4s.com/thumbs/trang-huy-hieu-the-loai-logo-2_thumb_150.jpg)
